The awk command is one of the most powerful text-processing tools in Linux. It allows you to manipulate, analyze, and extract data from text files or command output efficiently. This guide will walk you through the basics of awk, along with practical examples to help you understand its capabilities.
What is awk?
awk is a scripting language used for pattern scanning and processing. It reads input line by line, splits each line into fields, and allows you to perform operations on those fields using various built-in functions and expressions.
Basic Syntax
awk 'pattern { action }' filename- pattern: Defines a condition for executing the action.
- action: Specifies the operation to perform on matching lines.
- filename: The input file to process.
If no pattern is specified, awk executes the action for every line in the file.
Practical awk Examples
1. Print Specific Columns
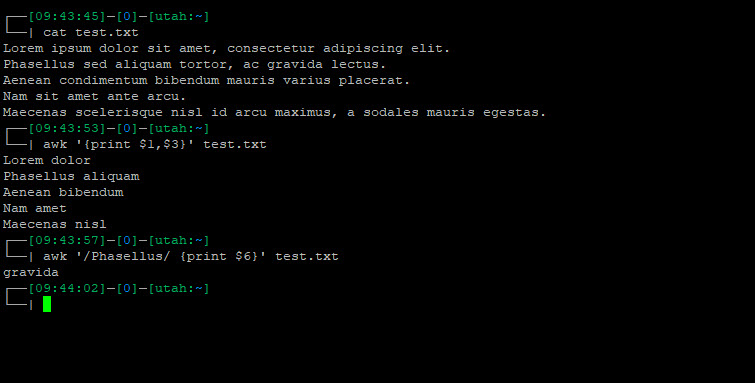
To print the first and third columns from a file with space-separated values:
awk '{print $1, $3}' data.txtThis command extracts and displays the first and third fields of each line.
2. Filter Data Using Conditions
Print only the lines where the second column is greater than 50:
awk '$2 > 50 {print $0}' data.txtHere, $2 > 50 acts as a condition, and {print $0} prints the entire matching line.
3. Use awk with cat or ls
awk can process command outputs. For example, listing files and filtering large ones:
ls -l | awk '$5 > 1000000 {print $9, $5}'This prints filenames and sizes of files larger than 1MB.
4. Find the Sum of a Column
To sum up the values in the second column:
awk '{sum += $2} END {print "Total:", sum}' data.txtThe END block runs after processing all lines, printing the total sum.
5. Use awk with Delimiters
For CSV files, specify the delimiter using -F:
awk -F, '{print $1, $3}' data.csvThis extracts columns from a comma-separated file.
6. Replace Text in a File
To replace “error” with “warning”:
awk '{gsub(/error/, "warning"); print}' log.txtThe gsub function finds and replaces text globally.
7. Count Occurrences of a Word
To count the number of times “Linux” appears in a file:
awk '/Linux/ {count++} END {print "Occurrences:", count}' file.txtThis script increments count for each occurrence and prints the result at the end.
Conclusion
The awk command is a versatile tool for processing structured text and automating data extraction tasks. By mastering its basic and advanced functionalities, you can streamline many Linux command-line operations.
Start experimenting with awk today, and you’ll see how it simplifies text processing tasks in your everyday workflow!